
Summary
Etomoxir is the first drug candidate out of a new class of substances -oxirane carboxylic acids – that has been developed in two clinical indications – diabetes type 2 and heart insufficiency – until phase II of clinical development. The substance acts as a irreversible inhibitor of the mitochondrial carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1 (E.C. 2.3.1.21), a regulatory enzyme of long-chain fatty acid oxidation. The real inhibitor is the Coenzyme A ester of the substance that is built in the cells.
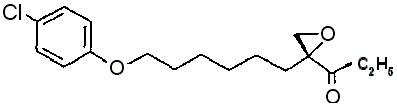
| INN: | Etomoxir (lat. etomixirum), Ethyl ( + )-2-[6-(parachlorphenoxy)hexyl]glycidat | |
| or | ||
| ( R )-( + )-2-[6-(4-Chlorphenoxy)hexyl]-oxiran-2-carbonsäure Ethylester | ||
| Mol. formula: | C17H23CIO4 | |
| Mol. wt.: | 326,8 | |
Mol. structure:
| Indications: | metabolic syndrome, heart insufficiency, diabetes type 2, ketoacidosis, hyperlipidemia, arteriosclerosis, coronary heart disease, inflammation, leukemia, dairy cow ketosis. | |
| Status: | phase II of clinical development. | |
| Dosis: | 2 x 40 mg until 2 x 80 mg daily. | |
| Drug form: | wet gelatin capsule | |
| Toxicology: | Acute toxicity: (LD50, fasted mice, rats, p. o.): 270 mg/kg. | |
| Sub acute toxicity: (LD50, rat, p. o.): > 125 mg/kg; (LD5, dog, p. o.): > 200 mg/kg. | ||
| No signs of mutagenicity, embryo-toxicity, and teratogenicity. | ||
